иғҢжҷҜзҹҘиҜҶпјҡ
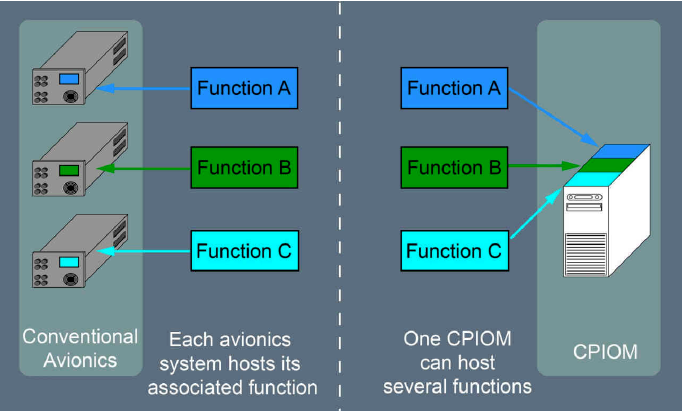
A350йҮҮз”ЁдәҶе…Ёж–°зҡ„иҲӘз”өзі»з»ҹи®ҫи®ЎпјҡIntegrated Modular Avionics (IMA). IMA е’Ңдј з»ҹиҲӘз”өзҡ„еҢәеҲ«е°ұеғҸжҳҜеҶҜиҜәдҫқжӣјз»“жһ„е’Ңд№ӢеүҚзҡ„и®Ўз®—жңәз»“жһ„д№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„еҢәеҲ«гҖӮдј з»ҹиҲӘз”өжҹҗдёӘ硬件е°ұеҜ№еә”жҹҗдёӘеҠҹиғҪпјҢд»ҺеӨ§е°ҸгҖҒеҶ…йғЁз»“жһ„гҖҒI/O зӯүи®ҫи®ЎдёҠеҸҜиғҪйғҪе®Ңе…ЁдёҚеҗҢпјҢиҲӘз”өд№Ӣй—ҙд№ҹеҸӘиғҪйқ з”өзјҶиҝһжҺҘпјҢиҖҢдё”з”өзјҶзҡ„и§„ж јеҸҜиғҪйғҪдёҚеҗҢгҖӮ
IMAжЁЎеқ—еҢ…жӢ¬ The Core Processing Input/Output Modules (CPIOMs) е’Ң The Common Remote Data Concentrators (CRDCs)
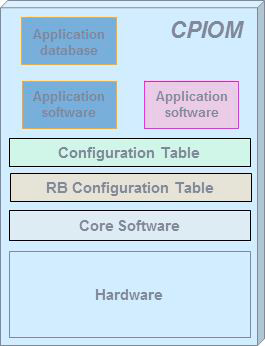
CPIOM зӣёеҪ“дәҺз»ҹдёҖзЎ¬д»¶и§„ж јпјҢз»ҹдёҖиҫ“е…Ҙ/иҫ“еҮәпјҲI/OпјүжҺҘеҸЈзҡ„йҖҡз”Ёи®Ўз®—жңәпјҢдёҚеҗҢзҡ„иҲӘз”өеҸӘжҳҜиЈ…еңЁдёҠйқўзҡ„иҪҜ件гҖӮеҰӮжһңдёҖдёӘзі»з»ҹзҡ„иҪҜ件жҜ”иҫғеӨҚжқӮпјҢеҚ з”Ёиө„жәҗиҫғеӨҡпјҢйӮЈеҸҜиғҪе°ұдёҖдёӘиҪҜ件用дёҖж•ҙдёӘCPIOMпјҢеҰӮжһңиҪҜ件жҜ”иҫғз®ҖеҚ•пјҢеҸҜиғҪе°ұеҮ дёӘиҪҜ件дёҖиө·иЈ…еңЁдёҖдёӘCPIOMдёҠгҖӮеӣ дёәжҳҜз»ҹдёҖй…ҚзҪ®е’Ң I/OпјҢCPIOMд№Ӣй—ҙзҡ„йҖҡи®Ҝд№ҹеҸҜд»Ҙз»ҹдёҖи§„ж јпјҢйқһеёёж–№дҫҝе®һзҺ° AFDX й«ҳйҖҹж•°жҚ®зҪ‘з»ңгҖӮ
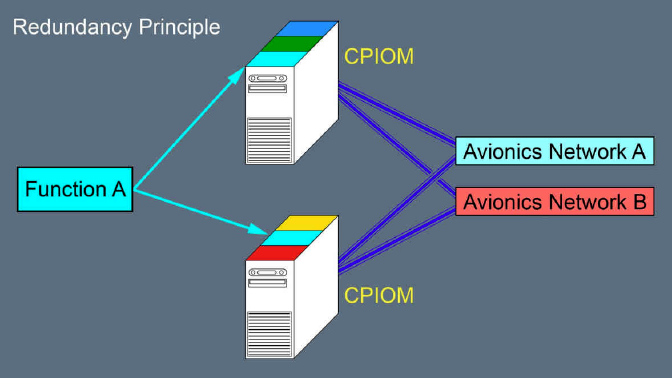
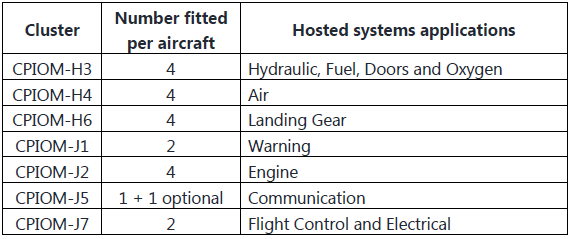
еҰӮдёҠйқўиҝҷдәӣеӣҫжүҖзӨәпјҢCPIOMе°ұжҳҜз”өи„‘пјҢдёҖдёӘCPIOMеҸҜд»ҘиЈ…еӨҡдёӘзі»з»ҹзҡ„иҲӘз”өзі»з»ҹиҪҜ件пјҢеҗҢж ·зҡ„иҪҜ件д№ҹеҸҜд»ҘиЈ…еңЁдёҚеҗҢзҡ„CPIOMдёӯпјҢдҪңдёәеҶ—дҪҷгҖӮCPIOM жңүдёӨзұ»пјҢH е’Ң JпјҢH зұ»жңү3з»„пјҢJзұ»жңү4з»„пјҢдёҖе…ұ7з»„гҖӮжҜҸдёҖз»„жңүдёҖдёӘжҲ–еӨҡдёӘCPIOMпјҢиҙҹиҙЈдёҖдёӘжҲ–еӨҡдёӘйЈһжңәзі»з»ҹзҡ„иҲӘз”өгҖӮ
еҮ дёӘиӯҰе‘Ҡпјҡ
еҫҲеӨҡзі»з»ҹжңүжң¬ең°жҺ§еҲ¶еҷЁпјҢеҚізЎ¬д»¶иҮӘеёҰзҡ„жҺ§еҲ¶еҷЁпјҢеҸҰеӨ–иҝҳжңүеңЁ CPIOM дёҠзҡ„жҺ§еҲ¶иҪҜ件пјҲapplicationsпјүгҖӮдёҖиҲ¬жқҘиҜҙпјҢжң¬ең°жҺ§еҲ¶еҷЁз”ЁдәҺеҹәзЎҖеҠҹиғҪпјҢжҺ§еҲ¶иҪҜ件用дәҺй«ҳзә§еҠҹиғҪгҖӮеҰӮжһңжҺ§еҲ¶иҪҜ件故йҡңдәҶпјҢжҲ–иҖ…жүҖеңЁзҡ„ CPIOM ж•…йҡңдәҶпјҢзі»з»ҹзҡ„еҹәжң¬еҠҹиғҪд»Қ然еҸҜд»Ҙе·ҘдҪңгҖӮ
дҪҶеңЁдёҚжӯЈеёёзЁӢеәҸдёӯпјҢз”ұдәҺе‘ҪеҗҚе’ҢжҸҸиҝ°еҺҹеӣ пјҢжңүзҡ„ең°ж–№еҫҲйҡҫеҲҶиҫЁеҮәеҲ°еә•жҳҜжң¬ең°жҺ§еҲ¶еҷЁиҝҳжҳҜ CPIOM иҪҜ件故йҡңгҖӮдёӢйқўд»Ҙз©әи°ғ/еўһеҺӢ/йҖҡйЈҺзі»з»ҹдёӯзҡ„дҫӢеӯҗжқҘиҜҙжҳҺгҖӮ
1 AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED MONITORING + CTL FAULT дёҺ AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED FAULT зҡ„еҢәеҲ«
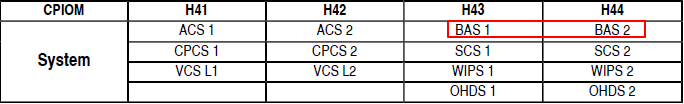
е®үиЈ…еңЁ H43 е’Ң H44 дёҠзҡ„ Bleed Air System (EBAS) еҰӮжһңж•…йҡңдәҶпјҢзӣёеә”еҸ‘еҠЁжңәеј•ж°”дёҖдәӣй«ҳзә§еҠҹиғҪпјҢжҜ”еҰӮзӣ‘жҺ§гҖҒйҡ”зҰ»гҖӮдҪҶеј•ж°”д»Қ然еҸҜд»Ҙд»ҘйҷҚзә§жЁЎејҸе·ҘдҪңпјҢеҺӢеҠӣжҺ§еҲ¶еҸҳжҲҗж°”еҠЁжЁЎејҸгҖӮ
иҖҢ AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED FAULT еҲҷжҳҜз”ұдәҺи¶…жё©гҖҒи¶…еҺӢгҖҒдҪҺеҺӢгҖҒзі»з»ҹжҺ§еҲ¶ж•…йҡңгҖҒеӨұеҺ»йҖҶжөҒдҝқжҠӨзӯүеҺҹеӣ дјҡеҜјиҮҙеӨұеҺ»еҸ‘еҠЁжңәеј•ж°”гҖӮеҸ‘еҠЁжңәеј•ж°”дјҡиҮӘеҠЁе…ій—ӯпјҢеҰӮжһңжІЎжңүе…іпјҢECAM зЁӢеәҸеҲҷиҰҒжұӮжңәз»„е…ій—ӯгҖӮиҝҷдёӘе°ұдёҚжҳҜ CPIOM иҪҜ件问йўҳдәҶгҖӮ
2 COND TEMP CTL FAULT дёҺз©әи°ғзі»з»ҹз« иҠӮжҸҗеҲ°зҡ„ pack controller дёҚжҳҜдёҖдёӘдёңиҘҝ
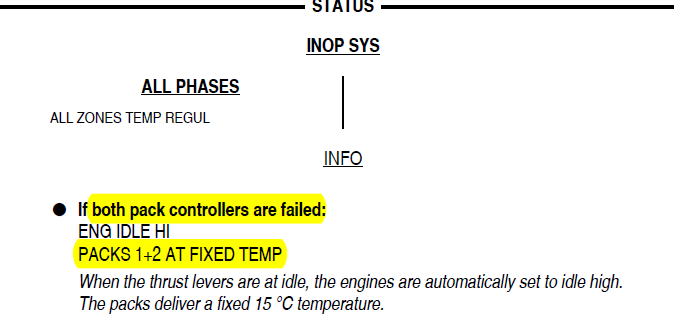
иҝҷдёӘиӯҰе‘Ҡзҡ„дёҚе·ҘдҪңзі»з»ҹдёӯжҸҗеҲ°дёӨйғЁ pack controller ж•…йҡңж—¶пјҢдёӨйғЁ PACK еҸӘиғҪжҸҗдҫӣеӣәе®ҡжё©еәҰгҖӮиҖҢеңЁзі»з»ҹз« иҠӮжҸҸиҝ°дёӯпјҢеҸҲжҸҗеҲ°еҰӮжһң pack controller ж•…йҡңпјҢзӣёе…і PACK е°ұеӨұеҺ»дәҶгҖӮ
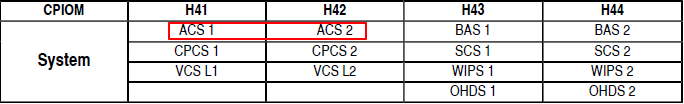
з©әе®ўеңЁеӣһеӨҚдёӯи§ЈйҮҠиҜҙзі»з»ҹз« иҠӮжҸҗеҲ°зҡ„ pack controller жҳҜжң¬ең°жҺ§еҲ¶еҷЁпјҢз§°дёә Air System Control Unit (ASCU)гҖӮ иҖҢ COND TEMP CTL FAULT иӯҰе‘Ҡдёӯзҡ„ pack controller жҳҜжҢҮ CPIOIM H41 е’Ң H42 дёҠе®үиЈ…зҡ„ Air Conditioning SystemпјҲACSпјүиҪҜ件гҖӮACS иғҪжҸҗдҫӣдјҳеҢ–ең°жё©еәҰжҺ§еҲ¶пјҢиҖҢ ASCU еҲҷиҙҹиҙЈеҹәжң¬еҠҹиғҪгҖӮиҮідәҺйғҪеҸ« pack controllerпјҢз©әе®ўиҜҙвҖңhowever, as both the ASCU and ACS are both pack controllers, we currently have no plans to revise the content.вҖқжҲ‘и§үеҫ—иҝҷеҫҲж•·иЎҚпјҢиҮіе°‘еҸҜд»ҘеҠ дёӘжӢ¬еҸ·ж ҮжіЁдёҖдёӢеҗ§гҖӮ
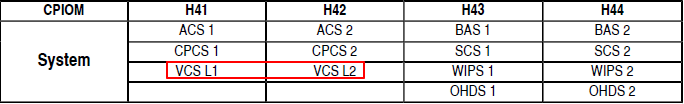
3 COND VENT CTL DEGRADED д№ҹеҸӘжҳҜ CPIOM дёӯзҡ„иҪҜ件故йҡң
Ventilation control system (VCS) жҳҜеңЁ CPIOM H4 дёҠзҡ„иҪҜ件пјҢжүҖд»Ҙе°ұз®—ж•…йҡңд№ҹдёҚжҳҜеҪ»еә•еӨұеҺ»йҖҡйЈҺеҠҹиғҪпјҢиҖҢеҸӘжҳҜ DEGRADEDпјҢеӨұеҺ»дёҖдәӣй«ҳзә§еҠҹиғҪпјҢжҜ”еҰӮ Air Management, Cabin Air Recirculation, Compartment Air Extraction, Commercial Equipment Ventilation, Cabin Crew Rest Compartment ventilation and all monitoring.
д»ҘдёӢжҳҜзӣёе…і TechRequest еҺҹж–ҮпјҢж–ҮдёӯеӣҫзүҮе°ұдёҚйҮҚеӨҚиҙҙеҮәдәҶпјҢеҸҜд»ҘеҸӮиҖғдёҠж–Үпјҡ
Q: AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED MONITORING + CTL FAULT
"The monitoring and the control of the engine 1(2) bleed air system is failed due to the failure of both EBAS control channels of the affected side."
"The monitoring capability and the isolation capability of the engine bleed air system are lost on the affected side. The temperature regulation is degraded."
What is the EBAS control channel? There's no description on DSC section. However it only need crew awareness. Is both EBAS control channels failure equal to Bleed air system control failure? If yes, what's the difference between AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED MONITORING + CTL FAULT and AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED FAULT? And is "crew awareness" means this problem affect a little or there'll be other detail alerts?
A:
Airbus has carefully reviewed your query and we would like to provide you with the following information:
The Engine Bleed Air System (EBAS) supplies high-pressure air to the different systems in the aircraft.
The EBAS control channel helps control and monitor the bleed air system. One control channel is hosted in the CPIOM H43 or H44 and CRDC B05 or B02 and the other control channel is hosted in the associated Bleed and Overheat Monitoring Units (BOMUs). Refer to CSC A350 FCOM Aircraft Systems/36-Bleed Air/Overview.
When both EBAS control channels fail, the monitoring capability and the isolation capability of the engine bleed air system are lost on the affected side. This will cause the AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED FAULT also. However, these two ECAM alerts are not exactly the same as the AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED FAULT could be caused by other failures too. Refer to AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED FAULT.
As there is no actions to be completed in flight, the ECAM alert AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED MONITORING + CTL FAULT only requires вҖңCrew AwarenessвҖқ.
Q_2:
So when both control channels fail, AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED MONITORING + CTL FAULT & AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED FAULT both will be triggered. That seems AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED MONITORING is just like a additional reminder. Be it so, why not set it as a subtitle of AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED FAULT?
A_2:
Please disregard our answer to Q1 in TechRequest 80763456/003.
First of all, we confirm that when AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED MONITORING + CTL FAULT triggers the AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED FAULT does no trigger the AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED FAULT.
When the EBAS control channel fails the monitoring capability and the isolation capability of the engine bleed air system are lost on the affected side but the bleed is still available. In degraded mode, the pressure control is in pneumatic mode. This means that the HP valve operates in pneumatic mode and regulates the downstream bleed pressure but the bleed is still available.
The main difference is that with AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED FAULT there will be no bleed air from the affected side. However, for AIR ENG 1(2) BLEED MONITORING + CTL FAULT the monitoring and isolation capability is failed but the bleed can still be provided in pneumatic control pressure mode.
Q: COND TEMP CTL FAULT
The situation after pack controller failure is incionsistent with description of DSC section. Does "pack is lost" means totally fail?
A:
The packs are controlled by two local controllers called Air System Control Unit (ASCU). The interface to other aircraft systems is realized via a Gateway through the CPIOMs. So, the sentence "pack controller fails" in FCOM PACKS system description is linked to the ASCU. If an ASCU Fails, the associated pack is lost. In case both CPIOMs are lost ("all ACS applications"), the ASCUs do not receive information from other aircraft systems, but the packs remain operative (in a backup mode).
Q_2:
According to your explanation, "If both pack controllers are fialed" in procedure meas CPIOMS failure insdead of ASCU failure. I think it's a bit confusing to crew. Can it be described more precise?
A_2:
We would like to clarify that the ASCUs and their related CPIOM ACS applications control and monitor the packs. As the condition in the ECAM alert refers to the failure of the ACS applications part of the pack controller, the temperature control (PACKS 1+2 operate at FIXED TEMP) is lost but the packs remain operative. In the Aircraft Systems/21 вҖ“ Air Conditioning/Air Condition Generation/Packs the sentence вҖңIn the event a pack controller fails, the associated pack is lost.вҖқ is the ASCU part that controls the pack. If the ASCU fails, the packs will be lost. We understand CSCs concern, however, as both the ASCU and ACS are both pack controllers, we currently have no plans to revise the content.
Q: COND VENT CTL DEGRADED
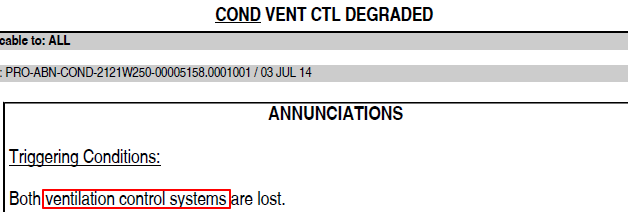
The triggering conditions: Both ventilation control systems are lost. Why does loss of both control systems only result CTL DEGRADED instead of FAULT?
A:
The ECAM alert COND VENT CTL DEGRADED is triggered if both CPIOMs, which are hosting the Ventilation Control System (VCS) application, are not operational or faulty OR both VCS applications have failed.
In this case the avionics ventilation, which is the most important function of the VCS, remains available in the default configuration. This is because no VCS software is needed to operate the avionics ventilation in the default configuration.
However, the function of the VCS is considered as DEGRADED because of a loss of Air Management, Cabin Air Recirculation, Compartment Air Extraction, Commercial Equipment Ventilation, Cabin Crew Rest Compartment ventilation and all monitoring. Apart from that, FWS and CDS indication is no longer available.